A Rare Case of Dapagliflozin-Induced Hepatic Toxicity
Um Caso Raro de Toxicidade Hepática Induzida por Dapagliflozina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24950/rspmi.2520Keywords:
Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury, Dapagliflozin, Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors/adverse effectsAbstract
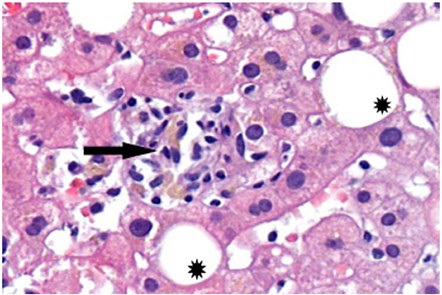
Drug-induced liver injury is a challenging clinical condition in terms of both diagnosis and treatment. It presents a wide range of clinical manifestations, and identification of the implicated substance is crucial. Several adverse effects have been described in association with dapagliflozin, but not liver enzyme elevation. The authors present the case of a 71-year-old diabetic woman who developed gastrointestinal symptoms one month after increasing the dose of dapagliflozin. Liver enzyme elevation was observed, without evidence of obstructive causes on imaging exams. Other causes of liver disease were excluded, and liver biopsy favored a toxic/drug etiology. Liver enzyme normalization was observed after discontinuation of dapagliflozin. Liver injury associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors is very rare, and the authors aim to raise awareness about the potential hepatotoxic effects of dapagliflozin, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Downloads
References
Nunes AL, Santos D, Figueiredo C, Ferreira DM, Lima J, Santos A. Um raro caso de hepatotoxicidade induzida pela empagliflozina. Med Interna. 2021;28:357-61. doi: 10.24950/rspmi.cc.131.4.2021.
LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors. [Updated 2023 Feb 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548289/
Ptaszynska A, Johnsson KM, Parikh SJ, de Bruin TW, Apanovitch AM, List JF. Safety profile of dapagliflozin for type 2 diabetes: pooled analysis of clinical studies for overall safety and rare events. Drug Saf. 2014;37:815-29. doi: 10.1007/s40264-014-0213-4.
Levine JA, Ann Lo A, Wallia A, Rogers M, VanWagner LB. Dapagliflozin-Induced Acute-on-Chronic Liver Injury. ACG Case Rep J. 2016;3:e169. doi: 10.14309/crj.2016.142.
Danan G, Teschke R. RUCAM in Drug and Herb Induced Liver Injury: The Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;17:14. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010014.
Hoofnagle JH, Björnsson ES. Drug-Induced Liver Injury - Types and Phenotypes. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:264-73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1816149.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol. 2019;70:1222-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.014.
Famularo G, Sajeva MR, Marino G, Granato C. Acute hepatitis caused by empagliflozin in a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patient. Ann Pharmacother. 2017;51:1142-3. doi: 10.1177/1060028017728522.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Internal Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





