Hepatopatia Glicogénica: Acidose Láctica Persistente em Diabético Tipo 1 Mal Controlado
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24950/rspmi.2627Palavras-chave:
Acidose Láctica, Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 1/complicações, Doença de Depósito de Glicogénio, Glicogénio Hepático, HepatomegaliaResumo
A síndrome de Mauriac é uma complicação rara da diabetes mellitus tipo 1 mal controlada e ainda é subdiagnosticada.
A hepatomegalia é um sinal típico e aparece na maioria dos doentes. Os sinais clínicos considerados típicos desta síndrome (baixa estatura, obesidade e hepatomegalia) são frequentemente incompletos e a acidose láctica pode ser exacerbada por terapêutica com altas doses de insulina e glicose, como acontece no curso do tratamento da cetoacidose diabética A hepatopatia glicogénica deve ser diferenciada da metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease como causa de hepatomegalia e anormalidades nas funções hepáticas
em doentes com diabetes mellitus tipo 1, uma vez que ambas exigem abordagens terapêuticas distintas e apresentam prognósticos diferentes.
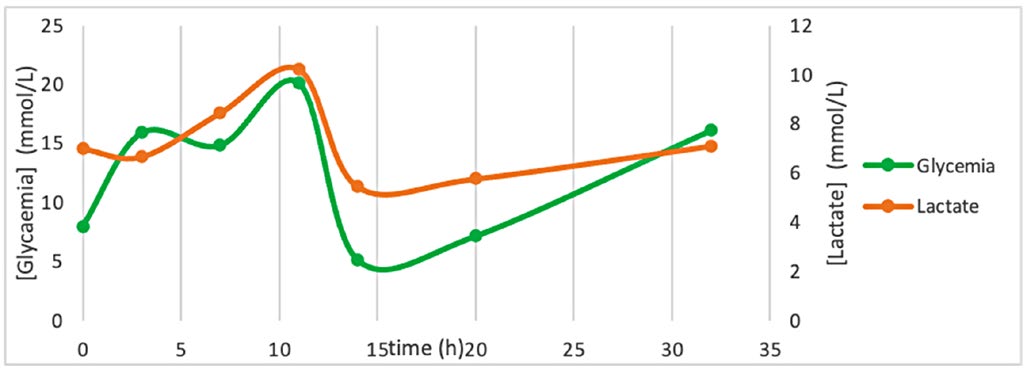
Os autores descrevem um caso clínico de acidose láctica persistente durante um episódio de cetoacidose diabética numa mulher com diabetes mellitus tipo 1 mal controlada, hepatomegalia e hepatopatia glicogénica que foi diagnosticada por biópsia hepática.
Downloads
Referências
Mauriac P. Gros ventre, hépatomégalie, troubles de la croissance chez les enfants diabétiques traités depuis plusieurs années par l'insuline. Gaz Hebd Sci Med Bordeaux. 1930;26:402–10.
Deemer KS, Alvarez GF. A Rare Case of Persistent Lactic Acidosis in the ICU: Glycogenic Hepatopathy and Mauriac Syndrome. Case Rep Crit Care. 2016; 2016:6072909. doi: 10.1155/2016/6072909.
Alhajjaj AH, Aljishi FK. Mauriac syndrome still exists in poorly controlled type 1 diabetes: a report of two cases and literature review. Cureus. 2021;13:e14704. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14704.
Singh Y, Gurung S, Gogtay M. Glycogen hepatopathy in type-1 diabetes mellitus: A case report. World J Hepatol. 2022;14:471-8. doi: 10.4254/wjh. v14.i2.471.
Asada S, Kawaratani H, Mashitani T, Kaya D, Nishigori M, Kubo T, et al. Glycogenic Hepatopathy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Intern Med. 2018;57:1087-92. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9490-17.
European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Association for the Study of Diabetes; European Association for the Study of Obesity. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Executive Summary. Diabetologia. 2024;67:2375-92. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06196-3. Erratum in: Diabetologia. 2024;67:2608. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06258-6
Messeri S, Messerini L, Vizzutti F, Laffi G, Marra F. Glycogenic hepatopathy associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus as a cause of recurrent liver damage. Ann Hepatol. 2012;11:554-8.
Sumida Y, Yoneda M. Glycogen Hepatopathy: An Under-recognized Hepatic Complication of Uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Intern Med. 2018;57:1063-64. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0051-17.
Reddy AJ, Lam SW, Bauer SR, Guzman JA. Lactic acidosis: Clinical implications and management strategies. Cleve Clin J Med. 201582:615-24. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.82a.14098.
Touilloux B, Lu H, Campos-Xavier B, Superti-Furga A, Hauschild M, Bouthors T, et al. Elevated lactate in Mauriac syndrome: still a mystery. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021;21:172. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00835-1. Erratum in: BMC Endocr Disord. 2021;21:194. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00858-8.
Subedi A, Kumar VCS, Sharma A, Hoilat G, John S. Persistent lactic acidosis in the Mauriac syndrome in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Proc. 2021;34:382-3. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1866936.
Ahmed HH, De Bels D, Attou R, Honore PM, Redant S. Elevated Lactic Acid During Ketoacidosis: Pathophysiology and Management. J Transl Int Med. 2019;7:115-7. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2019-0024.
Kocova M, Milenkova L. Old syndrome-new approach: Mauriac syndrome treated with continuous insulin delivery. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 20186:2050313X18785510. doi: 10.1177/2050313X18785510.
Abboud W, Abdulla S, Al Zaabi M, Moufarrej R. Young Man with Hepatomegaly: A Case of Glycogenic Hepatopathy. Case Reports Hepatol. 2018;2018:6037530. doi: 10.1155/2018/6037530.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Secção
Categorias
Licença
Direitos de Autor (c) 2025 Medicina Interna

Este trabalho encontra-se publicado com a Creative Commons Atribuição-NãoComercial 4.0.
Direitos de Autor (c) 2023 Medicina Interna
Acesso livre








